That analysis is generated using a number of different tools including Porter's Five Forces Framework, which analyzes the competitiveness of a brand.
The framework, created in 1972, by Harvard University's Michael E. Porter, seeks to determine a company's competitiveness intensity and attractiveness (or lack thereof) of an industry in terms of profitability.
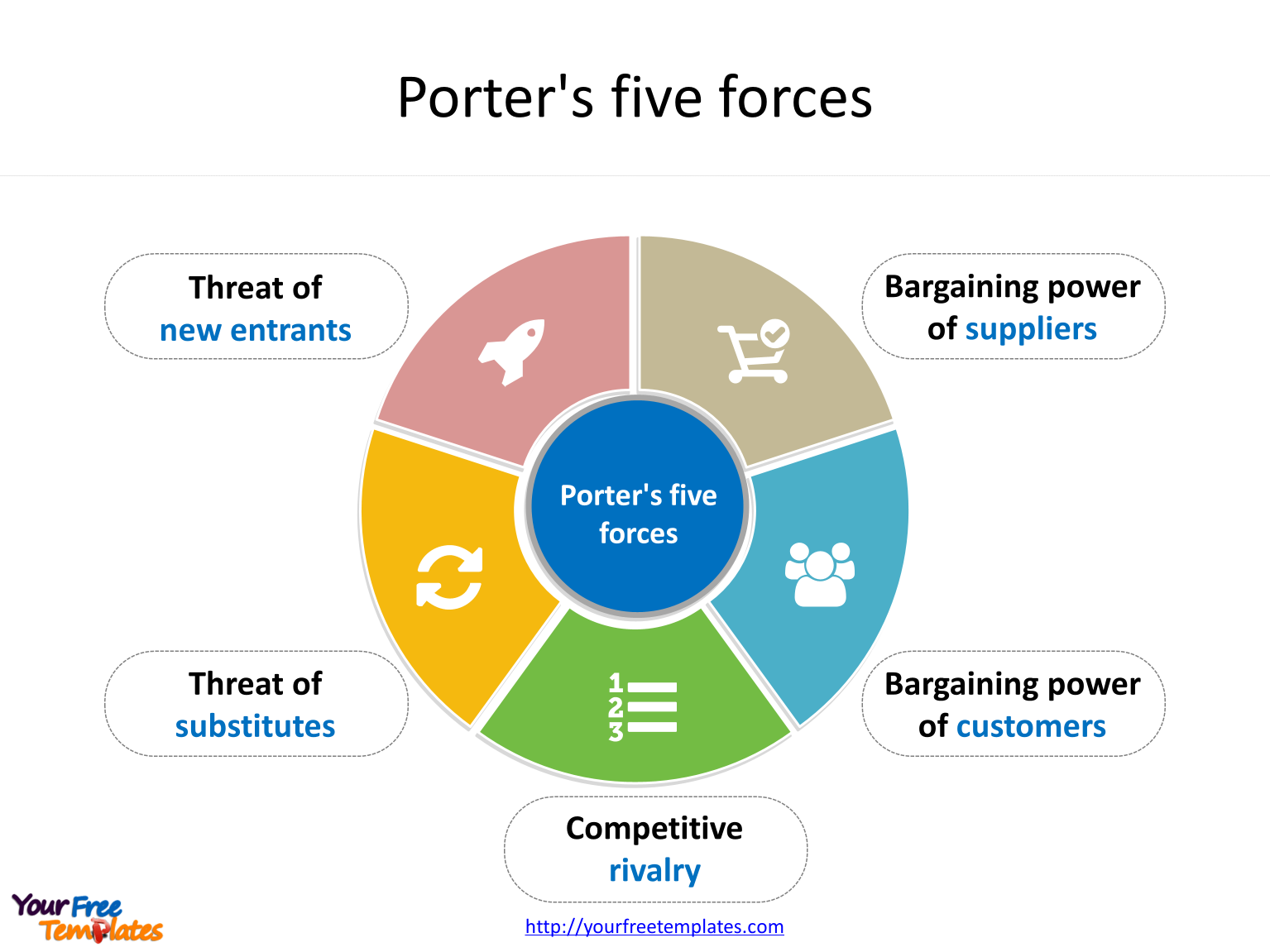
Porter's Five Forces include three forces from "horizontal" competition--the threat of substitute products or services, the threat of established rivals, and the threat of new entrants--and two others from "vertical" competition--the bargaining power of suppliers and the bargaining power of customers.
Let's consider each of these five forces in more detail:
1. Industry Rivalry (degree of competition among existing firms)
Intense competition leads to reduced profit potential for companies in the same industry.
2. Threat of Substitutes (products or services)
The availability of substitute products will limit your ability to raise prices.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
Powerful buyers have a significant impact on prices.
4. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Powerful suppliers can demand premium prices and limit your profit.
5. Barriers to Entry (threat of new entrants)
These act as a deterrent against new competitors.
A valuable tool in conducting industry research, Porter's Five Forces allow the marketer to adopt a strategy that best strengthens the company's position in the market.
Among the benefits of industry research, including the use of Porter's Five Forces, are:
- Keeping up with an audience’s communication style and medium
- Identify market opportunities
- Plan next marketing effort
Many tools exist to conduct industry research including:
- Social media monitoring
- Market research reports
- Search analytics
- Academic research
No comments:
Post a Comment